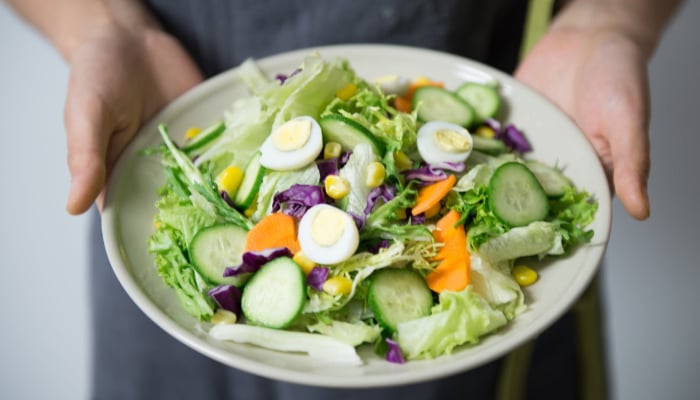
Salads have become a popular choice for those seeking a nutrient-packed, versatile meal. Rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, they can support overall wellness and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. But is eating salad every day truly beneficial? Let’s break it down.
Why Salads Are So Loved?
Most salads contain vegetables, fruits, beans, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds—all high in fiber. Fiber is crucial for digestive health, helps maintain a feeling of fullness, and supports healthy blood sugar levels. According to the 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, only about 5% of Americans meet their daily fiber needs 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men. Regularly eating salad can help fill that gap.
Getting enough fiber has also been linked with a lower risk of heart disease, diabetes, certain cancers, and may even contribute to a longer life.
The CDC reports that only 1 in 10 Americans consume the recommended five cups of fruits and vegetables daily. Since a typical salad contains at least 1–2 cups of leafy greens, eating one every day can help you reach your daily quota.
Leafy greens like spinach, romaine, arugula, and kale are rich in vitamins A, C, and E, which act as antioxidants and have anti-inflammatory benefits. Salads also provide essential minerals such as potassium, magnesium, and iron, all important for overall health.
Salads are highly versatile. You can adjust ingredients to fit dietary preferences, allergies, or digestive needs. For those with IBS or other gut sensitivities, selecting suitable vegetables and avoiding certain fibers can prevent discomfort.
How to Make Your Salad Healthy and Filling?
Many people believe salads are just “vegetables and nothing else,” which can leave you feeling hungry. Adding protein—like chicken, tofu, beans, eggs, or cheese—can increase satiety and make salads more filling. Healthy fats, such as avocado or nuts, can also boost nutrition and help absorb fat-soluble vitamins.
3 Tips for Enjoying Salad:
Build It: Start with your favorite greens and add proteins, vegetables, fruits, and healthy fats.
Change It: Turn your salad into a wrap or sandwich for variety.
Prep It: Layer salad ingredients in a mason jar for easy grab-and-go meals.
Can Eating Salad Help With Weight Loss?
Salads are naturally low in calories and high in fiber, which can help you feel full and reduce overall calorie intake. However, the impact on weight depends on what you add to your salad—heavy dressings, fried toppings, or excessive cheese can add calories quickly. Choosing nutrient-dense, whole ingredients is key.
Are There Any Risks?
While salads are generally safe, eating extremely large amounts of high-fiber vegetables all at once can cause digestive discomfort for some people. Additionally, always avoid ingredients that trigger allergies or sensitivities. For most people, including a salad as part of a balanced diet is safe and beneficial.
The Bottom Line:
Eating salad every day can be a healthy choice, supporting fiber intake, boosting fruit and vegetable consumption, and providing essential nutrients. By including a variety of colorful ingredients, proteins, and healthy fats, salads can be both satisfying and nutritious. Just remember: balance and variety are key—your salad should complement, not replace, a well-rounded diet.