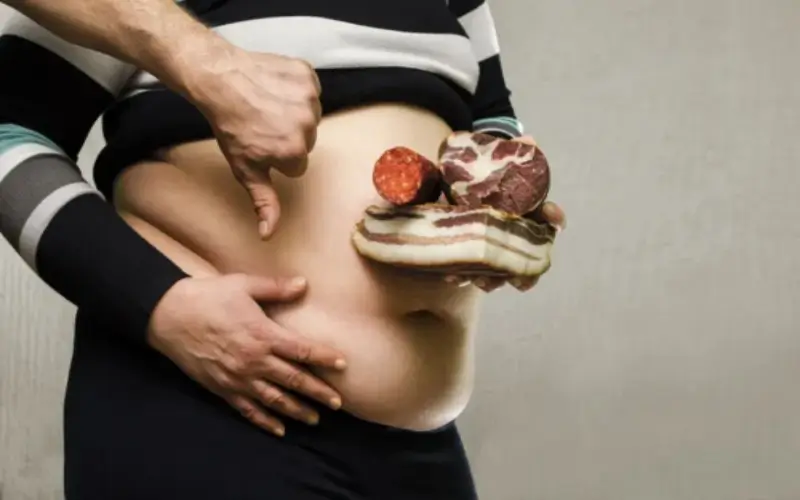
A healthy metabolism plays a key role in maintaining energy levels, managing weight, and supporting overall well-being.
However, many people unknowingly follow dietary habits that slow down their metabolism, making it harder to burn calories efficiently. Below are some common diet mistakes that can negatively affect metabolic speed.
One major mistake is eating too few calories. While cutting calories may seem like a quick way to lose weight, extreme calorie restriction signals the body to conserve energy. As a result, the metabolism slows down to protect vital functions. Over time, this can lead to fatigue, nutrient deficiencies, and weight gain once normal eating resumes.
Skipping meals is another habit that harms metabolism. When meals are missed, the body goes into a “starvation mode,” slowing calorie burning to preserve energy. Regular, balanced meals help keep blood sugar stable and metabolism active throughout the day.
Not eating enough protein can also reduce metabolic rate. Protein requires more energy to digest compared to fats and carbohydrates, a process known as the thermic effect of food. A low-protein diet may reduce muscle mass, which is crucial because muscle burns more calories than fat, even at rest.
Read more: Surprising health benefits of Orange juice
Relying heavily on processed and sugary foods is another common mistake. These foods are often low in fiber and nutrients, causing rapid spikes and drops in blood sugar. This can lead to energy crashes and poor metabolic efficiency. Whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins support a healthier metabolism.
Drinking too little water can also slow metabolism. Even mild dehydration can reduce the body’s ability to burn calories efficiently. Water is essential for digestion, nutrient absorption, and energy production, making hydration an important factor in metabolic health.
Another overlooked mistake is consuming too little fat. Healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, olive oil, and avocados, are necessary for hormone production. Hormones play a direct role in regulating metabolism, and a lack of healthy fats can disrupt this balance.
Excessive dieting without strength training is also problematic. Losing weight without maintaining muscle mass can slow metabolism over time. Diets that ignore resistance or strength exercises may lead to muscle loss, reducing the body’s calorie-burning ability.
Read more: Five foods and drinks to help soothe flu symptoms
Lastly, excessive consumption of alcohol can negatively impact metabolism. Alcohol provides empty calories and interferes with the body’s ability to burn fat efficiently. Regular overconsumption can slow metabolic processes and contribute to weight gain.
Metabolism is influenced not just by genetics but also by daily dietary choices. Avoiding extreme calorie cuts, eating balanced meals, staying hydrated, choosing whole foods, and supporting muscle health can help maintain a healthy and efficient metabolism. Making small, consistent improvements in diet can lead to long-term metabolic benefits.