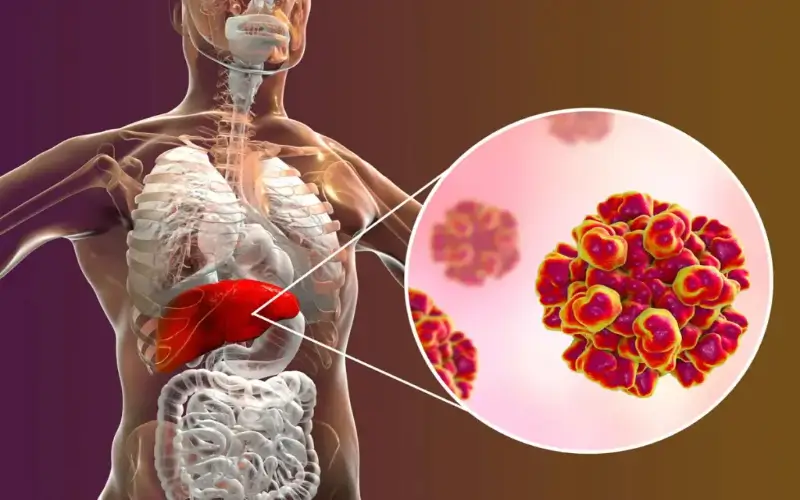
Hepatitis is a medical condition that refers to inflammation of the liver, a vital organ responsible for detoxifying the blood, producing essential proteins, and aiding in digestion. While the liver can handle minor damage, persistent inflammation caused by hepatitis can lead to serious health problems, including liver cirrhosis, liver failure, or even liver cancer.
Types of Hepatitis
Hepatitis can be caused by several factors, including viral infections, autoimmune diseases, and certain medications or toxins. The most common types are hepatitis A, B, and C:
Hepatitis A: This type is caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV) and usually spreads through contaminated food or water. It is generally acute and does not lead to chronic liver disease. Vaccination can prevent hepatitis A effectively.
Hepatitis B: Caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), this form can be both acute and chronic. It spreads through blood, or from mother to child during childbirth. Chronic hepatitis B can lead to serious liver complications if not treated properly. Vaccination is available and is highly effective.
Hepatitis C: Caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV), this type is mainly transmitted through blood, including unsafe injections or transfusions. Hepatitis C often becomes chronic, leading to long-term liver damage. Although there is no vaccine, modern antiviral treatments can cure most cases.
Other less common types include hepatitis D and E. Hepatitis D occurs only in people already infected with hepatitis B, while hepatitis E spreads through contaminated water and is usually self-limiting.
Symptoms of Hepatitis
Hepatitis symptoms can range from mild to severe. Some people may remain asymptomatic, especially in the early stages. Common symptoms include:
Fatigue and weakness
Nausea and vomiting
Loss of appetite
Abdominal pain, especially near the liver
Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
Dark-colored urine and pale stools
Fever and joint pain
Since the symptoms can resemble other illnesses, testing and diagnosis by a healthcare professional are essential.
Causes and Risk Factors
Viral infections are the most common cause of hepatitis, but other factors can contribute:
Excessive alcohol consumption: Can lead to alcoholic hepatitis.
Autoimmune hepatitis: Occurs when the immune system attacks liver cells.
Medications and toxins: Certain drugs and chemicals can damage the liver.
Risk factors include sharing needles, poor sanitation, and travel to areas where hepatitis is common.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment depends on the type and severity of hepatitis. Acute hepatitis may resolve on its own, but chronic forms require medical management. Antiviral medications can control hepatitis B and often cure hepatitis C. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding alcohol, maintaining a healthy diet, and regular exercise, support liver health.
Prevention is crucial and includes vaccination for hepatitis A and B, avoiding sharing needles, and ensuring safe food and water consumption. Routine screening, especially for high-risk groups, helps in early detection and management.
Hepatitis is a serious liver condition with various causes, types, and symptoms. Awareness, timely diagnosis, proper treatment, and preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve overall liver health. Regular check-ups, vaccinations, and a healthy lifestyle are essential to protect against this silent but potentially dangerous disease.