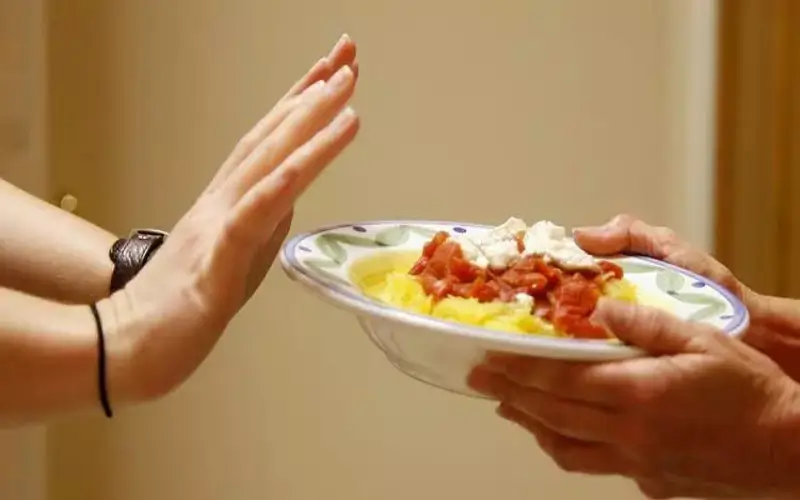
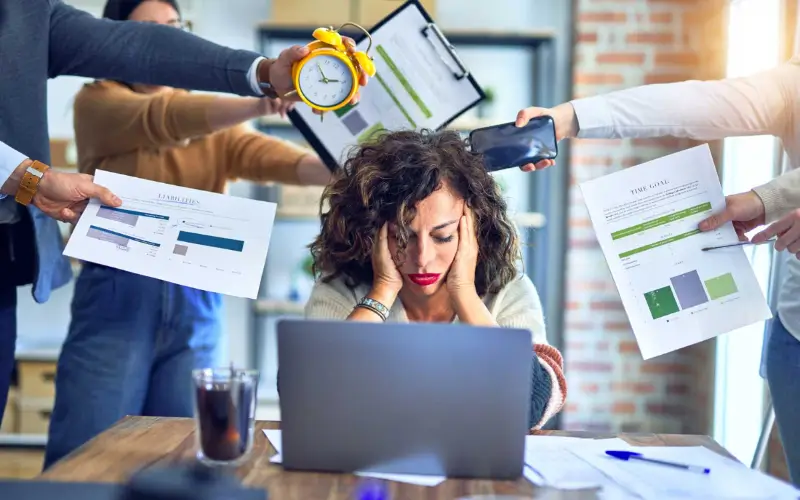
Skipping meals damages health by causing nutrient deficiencies, slowing metabolism (leading to weight gain), creating blood sugar spikes and crashes, impairing brain function (brain fog, poor focus), triggering stress hormones, and increasing risks for diabetes, heart issues, and poor gut health, often leading to overeating unhealthy foods later. Regular, balanced meals provide steady fuel, prevent energy slumps, and support overall metabolic and cognitive health, making it crucial for weight management and well-being.
Skipping meals may seem harmless or even helpful for saving time or managing weight, but doing so regularly can negatively affect both your body and mind. Below are ten common side effects of missing meals.
1. Low Energy Levels
When you skip meals, your body lacks the fuel it needs to function properly. This often leads to constant tiredness, weakness, and reduced stamina throughout the day.
2. Poor Concentration
Your brain relies on a steady supply of glucose. Missing meals can cause difficulty focusing, slow thinking, and reduced productivity.
3. Increased Irritability and Mood Swings
Hunger can affect your emotions. Skipping meals may lead to irritability, anxiety, and sudden mood changes due to unstable blood sugar levels.
4. Slower Metabolism
Regularly skipping meals can slow down your metabolism as the body tries to conserve energy, making weight management more difficult.
5. Overeating Later
Missing meals often leads to extreme hunger later in the day, increasing the risk of overeating or making unhealthy food choices.
6. Digestive Problems
Skipping meals can disrupt digestion, causing issues such as acidity, bloating, constipation, or stomach discomfort.
Read more: How quality sleep improves physical and mental health
7. Weak Immune System
Inadequate nutrition weakens the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to infections and illnesses.
8. Blood Sugar Imbalances
Skipping meals can cause sudden drops or spikes in blood sugar levels, which may be especially dangerous for people with diabetes.
9. Muscle Loss
When the body doesn’t get enough energy from food, it may start breaking down muscle tissue for fuel, leading to muscle weakness over time.
10. Hormonal Imbalance
Irregular eating habits can disrupt hormone production, affecting sleep, appetite, stress levels, and overall health.
Read more: How just 10 minutes of exercise improves health
Skipping meals occasionally may not cause serious harm, but making it a habit can lead to long-term health problems. Eating regular, balanced meals helps maintain energy, supports mental clarity, and keeps the body functioning at its best.