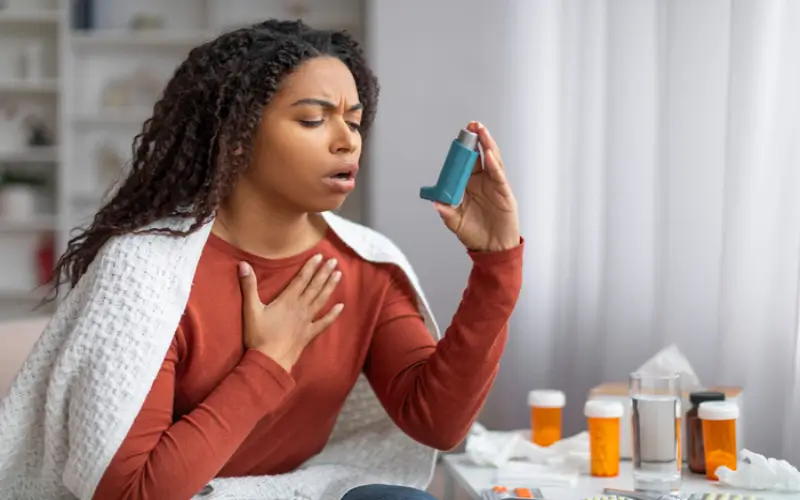
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. While asthma cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed with a consistent health routine. A well-planned daily routine helps reduce flare-ups, improve lung function, and enhance overall quality of life.
A strong asthma management routine begins with understanding your triggers. Common triggers include dust, pollen, smoke, pet dander, cold air, respiratory infections, and strong odors. Keeping a symptom diary can help identify patterns and specific triggers. Once identified, minimizing exposure is essential. For example, using dust-proof mattress covers, washing bedding weekly in hot water, and keeping windows closed during high pollen seasons can significantly reduce symptoms.
Medication adherence is a crucial part of asthma management. Most patients are prescribed two types of inhalers: a daily controller inhaler (often containing corticosteroids) to reduce inflammation, and a rescue inhaler for quick relief during sudden symptoms. It is important to take controller medication exactly as prescribed, even when feeling well. Skipping doses can increase the risk of attacks. Always carry a rescue inhaler and ensure it is not expired.
Regular monitoring of lung function is another key habit. Using a peak flow meter at home helps track breathing capacity and detect early warning signs of worsening asthma. Recording peak flow readings daily allows you to recognize when action is needed before symptoms become severe. Following a personalized asthma action plan, created with your healthcare provider, ensures you know exactly what steps to take during different stages of symptoms.
Exercise is beneficial for overall health and can improve lung capacity, but it should be approached carefully. Choose moderate activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling. Warming up before exercise and using a prescribed inhaler beforehand can prevent exercise-induced symptoms. Swimming is often recommended because warm, humid air is less likely to trigger airway irritation. However, always consult a doctor before starting a new fitness routine.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a supportive role in asthma control. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports immune function and reduces inflammation. Staying hydrated helps keep mucus thin and easier to clear from the airways. Adequate sleep is equally important, as fatigue can worsen symptoms. Aim for seven to eight hours of quality sleep each night.
Stress management is often overlooked but highly important. Emotional stress can trigger asthma symptoms in some individuals. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation can help control stress levels. Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke is non-negotiable, as tobacco smoke is a major asthma trigger and can severely damage lung health.
Finally, regular medical check-ups are essential. Routine visits allow healthcare providers to adjust medications, review inhaler techniques, and monitor overall control. Vaccinations, including annual flu shots, are recommended to prevent respiratory infections that can worsen asthma.
By following a structured daily health routine, individuals with asthma can significantly reduce symptoms and live active, fulfilling lives. Consistency, awareness, and proactive care are the foundation of effective asthma management.