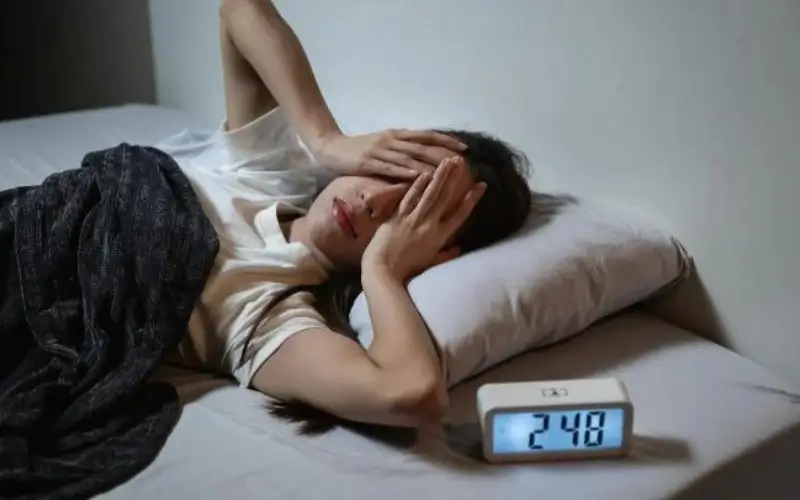
Sleep is a fundamental biological need, just like food and water. Yet, in today’s fast-paced lifestyle, many people sacrifice sleep due to work pressure, screen time, stress, or social commitments. Chronic sleep deprivation can have serious consequences for both mental and physical health, affecting overall quality of life.
Sleep deprivation occurs when a person does not get enough sleep to function properly. Most adults need 7–9 hours of sleep per night, while teenagers and children need even more. Missing sleep occasionally may cause temporary tiredness, but long-term sleep deprivation can lead to severe health issues.
Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Mental Health
One of the earliest and most noticeable impacts of sleep deprivation is on mental health. Lack of sleep affects brain function, emotional regulation, and decision-making abilities.
Sleep deprivation increases the risk of mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. When the brain does not get adequate rest, it struggles to manage stress and emotions effectively. This can result in mood swings, irritability, and heightened emotional sensitivity.
Cognitive functions such as memory, concentration, and problem-solving also decline. People who are sleep-deprived often experience difficulty focusing, slower reaction times, and poor judgment. Over time, chronic sleep loss may contribute to burnout and reduced productivity at work or school.
Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Physical Health
Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining physical health by supporting the immune system, metabolism, and cardiovascular function. When sleep is consistently lacking, the body’s natural repair processes are disrupted.
One major consequence is a weakened immune system. People who do not get enough sleep are more prone to infections such as colds and flu, and they may take longer to recover from illnesses.
Sleep deprivation also affects heart health. Studies have linked insufficient sleep to high blood pressure, increased risk of heart disease, and stroke. Additionally, poor sleep disrupts hormone balance, leading to weight gain by increasing hunger hormones and reducing feelings of fullness.
Read more: Every second woman in Pakistan suffers from Anaemia
Impact on Energy and Daily Performance
Lack of sleep significantly reduces energy levels and physical performance. People may feel constant fatigue, low motivation, and reduced stamina throughout the day. This can increase the risk of accidents, especially while driving or operating machinery, due to slower reaction times and reduced alertness.
Athletes and physically active individuals may also experience decreased muscle recovery and lower performance levels when sleep is inadequate.
Long-Term Health Risks
Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to serious long-term health conditions. These include diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease, and even cognitive decline in later life. Over time, the combined effects on mental and physical health can reduce life expectancy and overall well-being.
Read more: 7 detox water recipes to boost energy and immunity
Sleep deprivation is not just an inconvenience; it is a serious health concern. It negatively affects mental health, physical well-being, daily performance, and long-term health outcomes. Prioritizing quality sleep by maintaining a regular sleep schedule, reducing screen time before bed, and managing stress can significantly improve overall health. Adequate sleep is essential for a healthy mind and body.