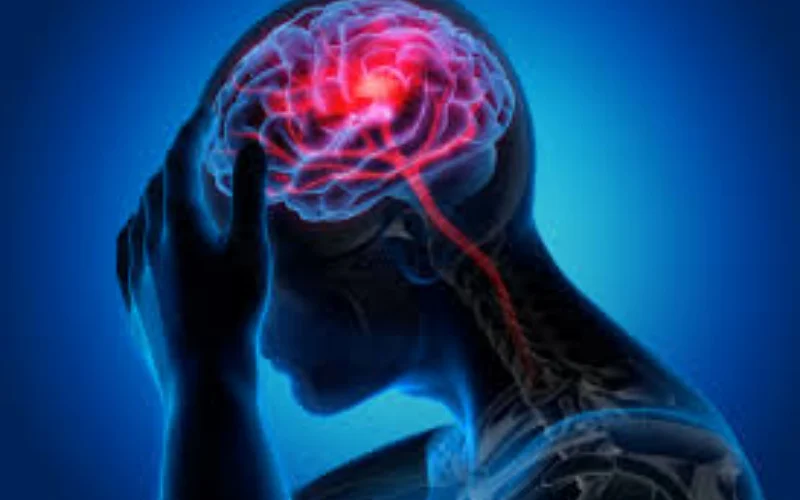
Adopting a specific dietary pattern may significantly reduce the risk of life-threatening conditions such as stroke, health experts say, citing new research published in the medical journal Neurology Open Access.
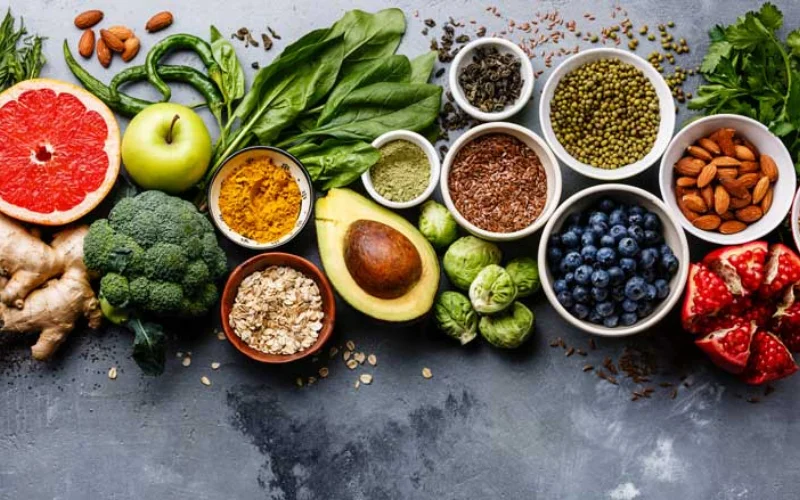
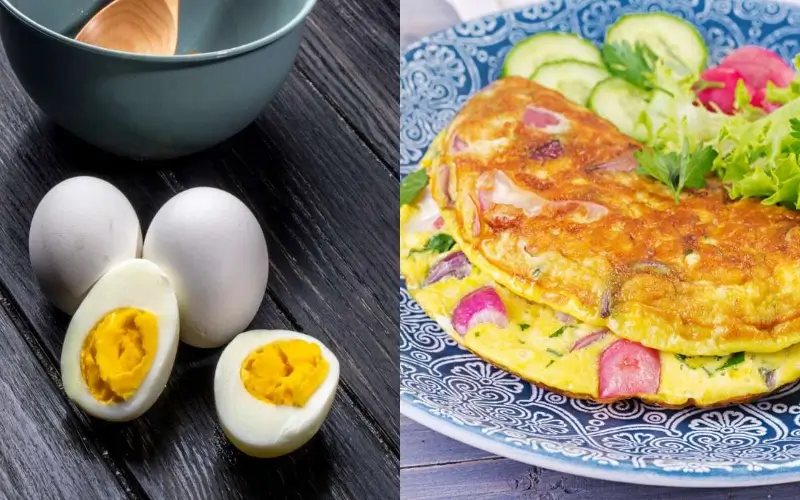
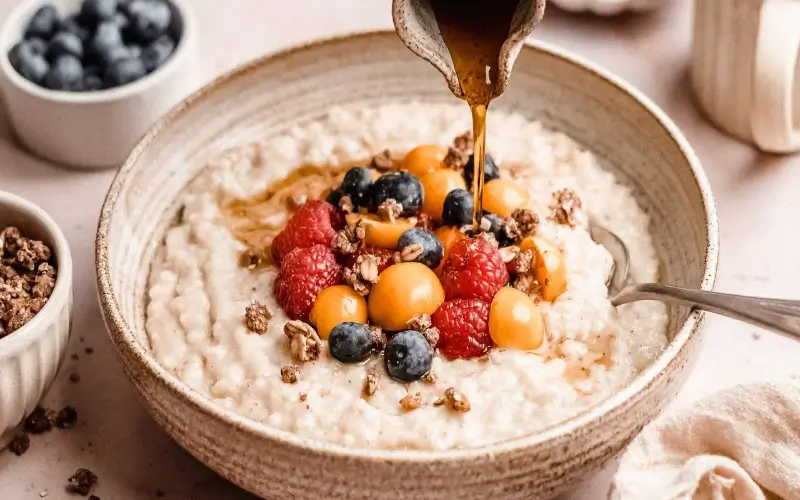
According to the study, the Mediterranean diet, commonly followed in countries such as Spain, Greece, Italy, and France, can substantially lower the risk of various types of stroke in women.
The diet primarily consists of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, fish, and olive oil, while the intake of red meat is kept to a minimum.
Researchers noted that this balanced dietary combination not only reduces the risk of the most common type of stroke but also lowers the chances of brain hemorrhage, a form of stroke caused by bleeding in the brain.
The findings reinforce the growing body of evidence highlighting the importance of healthy eating habits in stroke prevention.
Experts emphasized that the association between diet and reduced risk of brain hemorrhage is particularly noteworthy, as fewer studies in the past have focused on dietary impacts on this type of stroke.
The study included more than 105,000 women with an average age of 53 years, none of whom had a prior history of stroke at the start of the research.
Participants provided detailed information about their daily dietary habits through questionnaires and were followed for 21 years.
During the follow-up period, 4,083 women experienced a stroke. After accounting for various influencing factors, researchers concluded that women who consistently adhered to the Mediterranean diet had a 16 to 25 percent lower risk of developing different types of stroke.
Medical experts reminded that stroke remains one of the leading causes of death and long-term disability worldwide.
However, they stressed that the risk of this deadly condition can be reduced to some extent through balanced and healthy nutrition.
While the results are encouraging, researchers said further studies are needed to better understand the biological mechanisms through which the Mediterranean diet offers protection against stroke, which could help develop more effective dietary guidelines in the future.