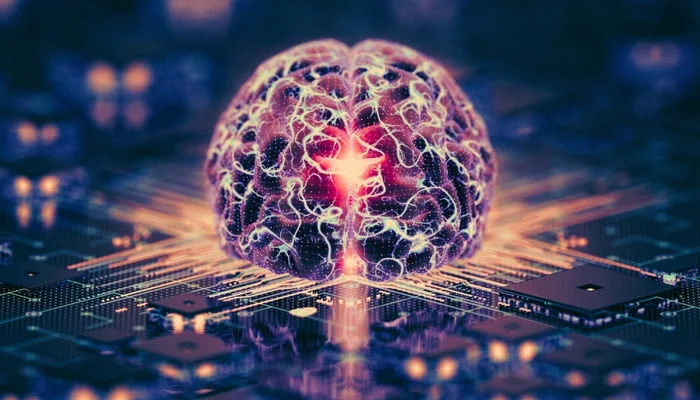
A new technological frontier is rapidly taking shape as scientists move from silicon chips to computers built with human brain cells. A development now known as bio-computing.
While still in its early stages, these “living computers” have already demonstrated capabilities such as playing simple games and performing basic speech-recognition tasks.
Researchers say interest in bio-computing has surged for three major reasons: rising investment across all areas of artificial intelligence, unexpected advances in lab-grown brain tissue, and breakthroughs in brain–computer interfaces that are blurring the line between humans and machines.
For nearly 50 years, neuroscientists have grown neurons on electrodes to study their activity. The field accelerated in the 2000s when two-way communication between living neurons and computers was first achieved.
A major leap came in 2013, when scientists announced that stem cells could self-organize into three-dimensional brain-like structures called organoids. These organoids are now widely used for drug testing and disease research, though they show no signs of consciousness.
Read more: Chinese researchers develop 3D Screen you can move around with
In 2022, Australian company Cortical Labs reported that lab-grown neurons could play the video game Pong, a claim that sparked global excitement — and caution from experts who warned against interpreting this as the start of consciousness. The term “organoid intelligence” soon followed, but researchers acknowledge that current systems remain far behind even basic AI.
Meanwhile, commercial and academic interest continues to outpace ethical debate. Companies in the United States, China, Switzerland and Australia are racing to build more advanced bio-computing systems.
At UC San Diego, scientists have proposed using organoid-based computing to predict oil spills in the Amazon by 2028.
Experts emphasize that today’s bio-computers exhibit neither consciousness nor advanced intelligence only limited learning based on external stimuli.
The technology is still young, but its rapid progress suggests that debates about consciousness, moral status and the use of human biological material in machines may arrive far sooner than expected.
Read more: Samsung Galaxy launches TriFold phone with a huge 10-Inch screen